Impartiality is still key for news audiences. Here’s how to rethink it for the digital age
Our research shows people still value the ideal of impartial news. A new report offer suggestions to adapt it to a challenging environment
Most people agree that news organisations and journalists should reflect all sides of an issue and not push a particular agenda – at least when asked about it in surveys. Our 2021 Digital News Report finds this to be true across countries and age groups.
However, many people feel that the media often fail to live up to this ideal. Our surveys consistently show that committed partisans believe that traditional media coverage is unfair, especially in countries where debates about politics or social justice have become deeply polarised. In recent years we’ve also seen an increase in opinion-led television formats such as Fox News/MSNBC in the United States, GB News in the UK and CNews in France, while many traditional print publications have focussed on distinctive and robust opinion as a way of standing out online.
Together with the growth of partisan websites, YouTubers and podcasters, audiences now have access to a wider range of views than ever before. Against this background, some have questioned traditional approaches to impartiality that try to represent all points of view within a single broadcast or publication. Other critics go further – arguing that impartiality has given extreme or unrepresentative views undue prominence, through its focus on balance, helping to legitimise climate change deniers and anti-vaxxers amongst others.
This all raises the question: how relevant is impartial and objective journalism to audiences today? The Reuters Institute commissioned market research company JV Consulting to carry out qualitative research in four countries – Brazil, Germany, the UK, and the US – with different news markets, traditions of public broadcasting, and systems of media regulation. They conducted a series of focus groups and in-depth interviews on our behalf in February and March 2021 with politically and ethnically diverse groups of older and younger people interested in and engaged with news (52 people in total).
These are some of the key findings of the report:
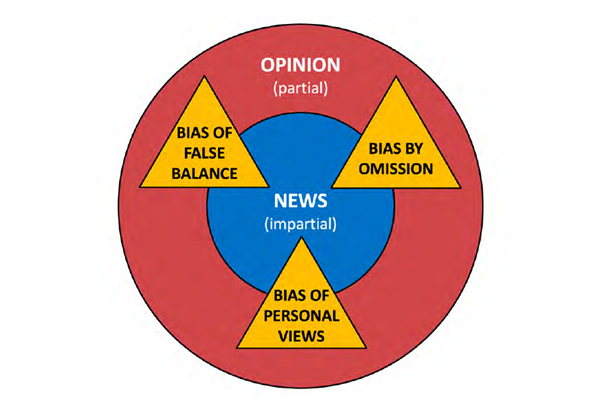
- Engaged audiences in the four countries researched still care about impartiality and say it helps define news, even if some consider it an impossible ideal. They want journalists to focus on facts, objectivity and fairness, and to steer clear of opinions and bias in reporting, leaving them to decide for themselves how they feel about the news. Alongside accuracy, impartiality is a foundational value of news that underpins audiences’ trust.
- People recognise the risk of giving exposure to extreme views or one side in the name of balance. However, evidence from this group of engaged users is that they are even more concerned about the suppression and silencing of viewpoints. There are particular misgivings about this in Brazil and Germany, where twentieth century history frames some people’s views.
- Most participants recognise that there were some topics (e.g., science stories, natural disasters, and questions of social justice) where there were not always two or more sides to represent. Here, many felt there should be more latitude for journalists to present just one perspective or an established point of view. There are also expectations that journalists will show greater empathy and connection in their reporting than perhaps traditional interpretations of impartiality have allowed in the past.
- Across countries, newer digital formats such as social media are perceived as carrying more risk of bias along with the growth of more informal and entertaining broadcast formats such as chat shows and podcasts. Impartiality is more vulnerable in these contexts, as well as when the news is emotive or controversial, because journalists’ personal views risk slipping out in the impulse to engage, although the subject and intention have a bearing on how audiences feel about this.
- Younger people, who have grown up using more informal and digital sources, tend to have different expectations of impartiality, often looking for journalism that aligns with their values. But overall, their underlying attitudes and desires are remarkably similar to older people’s.
- Different countries’ news traditions shape people’s experiences and expectations. Audiences in the US cannot envisage a world without partisan news outlets, but in the UK and Germany, with their public service traditions, most audiences still laud the upholding of impartiality.
- Respondents also delineate between news reporting (where impartiality is expected) and opinion/commentary (where people expect that views are argued for). Importantly, many told us that they often find it difficult to distinguish between the two, especially online. Interviewees like news and they like opinion, but want them very clearly separated.
It is important to recognise that not all news organisations are committed to impartiality: indeed, some make a virtue of creating news and opinion with a clear point of view. But most will want to take note of audience desires for a range of views to be represented and to see clearer labelling of news and opinion. For news organisations that are committed to impartiality, the report highlights the increased dangers in areas where journalism is more informal or accessed in distributed environments. Public media like the BBC have already embarked on updated training and issued new guidelines on these issues. Audiences have also sent a clear signal in this report that they would like much greater transparency over why certain perspectives are included or excluded, however difficult this may be in practice.
Finally, the report notes that given the importance of social media, search and other access points, technology platforms such as Facebook, Google and Apple, will also need to develop clearer guidelines on impartiality – as their own trust levels will depend on fair implementation of policies around inclusion and exclusion, whether by algorithm or human intervention.
Lire : Reuters Institute du 19 octobre
Télécharger : le rapport (68 pages)